400
Bad Request
Specifica del codice di stato HTTP 400
Fonte / Citazione da: Il codice di stato HTTP 400 Bad Request è specificato dalla sezione 6.5.1 di RFC7231.
Protocollo HTTP
Come lanciare un codice di stato 400 con PHP?
Per lanciare il codice di stato HTTP 400 su una pagina web, si può usare la funzione PHP http_response_code. La sintassi è la seguente: http_response_code(400) (PHP 5 >= 5.4.0, PHP 7, PHP 8)
Test del codice di stato HTTP 400
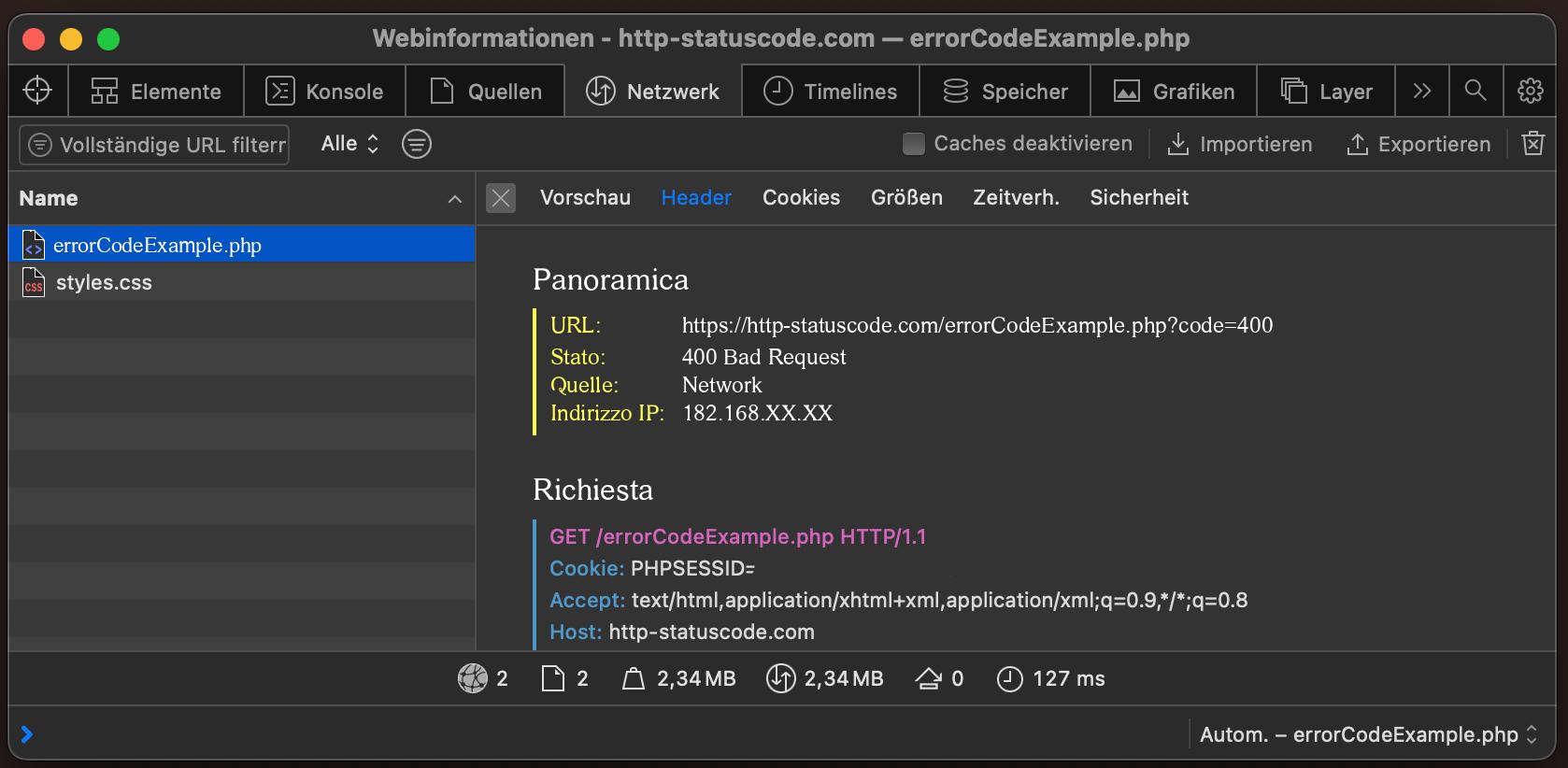
Per poter visualizzare il codice di stato HTTP (in questo caso 400 Bad Request) e altre informazioni sul lato client, è necessario aprire la console di sviluppo con F12. Quindi navigare nella scheda "Rete". Ora la pagina può essere aperta, il sito web (ad esempio index.php) dovrebbe essere visibile nella scheda Rete. Questo deve essere selezionato e poi deve essere selezionata la sezione Herder. L'utente vedrà quindi il seguente risultato:
URL: https://http-statuscode.com/errorCodeExample.php?code=400
Stato: 400 Bad Request
Quelle: Network
Indirizzo IP: XX.XX.XX.XX
Come creare la propria pagina di errore per il codice di stato 400
Apache Webserver
Il server web "Apache" è uno dei server web più comuni su Internet. Per creare la propria pagina di errore 400 Bad Request in "Apache", è necessario apportare la seguente modifica al file seguente.
NGINX Webserver
Simile al server web "Apache", anche "NGINX" è ampiamente utilizzato su Internet. Per creare la propria pagina di errore 400 Bad Request in "NGINX", è necessario apportare la seguente modifica al file seguente.
location = /400.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
internal;
}
Compatibilità con i browser del codice di stato 400
| Chrome | no data |
| Edge | no data |
| Firefox | no data |
| Opera | no data |
| Safari | no data |
| Chrome Android | no data |
| Firefox for Android | no data |
| Opera Android | no data |
| Safari on iOS | no data |
| Internet | no data |
| WebView Android | no data |
Costanti nei linguaggi di programmazione
HttpStatusCode.BadRequest
:not_modified
http.StatusBadRequest
response::HTTP_BAD_REQUEST
httplib.BAD_REQUEST
http.client.BAD_REQUEST
http.HTTPStatus.BAD_REQUEST
:bad_request
Codici di stato secondari del codice di stato 400
| 400.1 | Invalid Destination Header HTTP IIS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.2 | Invalid Depth Header HTTP IIS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.3 | Invalid If Header HTTP ISS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.4 | Invalid Overwrite Header HTTP ISS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.5 | Invalid Translate Header HTTP ISS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.6 | Invalid Request Body HTTP ISS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.7 | Invalid Content Length 400, Non ufficiale |
| 400.8 | Invalid Timeout HTTP ISS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.9 | Invalid Lock Token HTTP IIS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.10 | Invalid X-Forwarded-For (XFF) header HTTP ISS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.11 | Invalid WebSocket request HTTP IIS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.601 | Bad client request (ARR) HTTP ISS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.602 | Invalid time format (ARR) HTTP IIS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.603 | Parse range error (ARR) HTTP IIS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.604 | Client gone (ARR) HTTP IIS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.605 | Maximum number of forwards (ARR) HTTP IIS, Non ufficiale |
| 400.606 | Asynchronous competition error (ARR) HTTP IIS, Non ufficiale |
