Specification of the HTTP status code 400
Source / Quote by: The 400 Bad Request HTTP Status Code is specified by section 6.5.1 of RFC7231.
HTTP-Protocol
How to throw a 400 statuscode with PHP?
To throw the HTTP status code 400 on a web page, the PHP function http_response_code can be used. The syntax is as follows: http_response_code(400) (PHP 5 >= 5.4.0, PHP 7, PHP 8)
Test the 400 HTTP status code
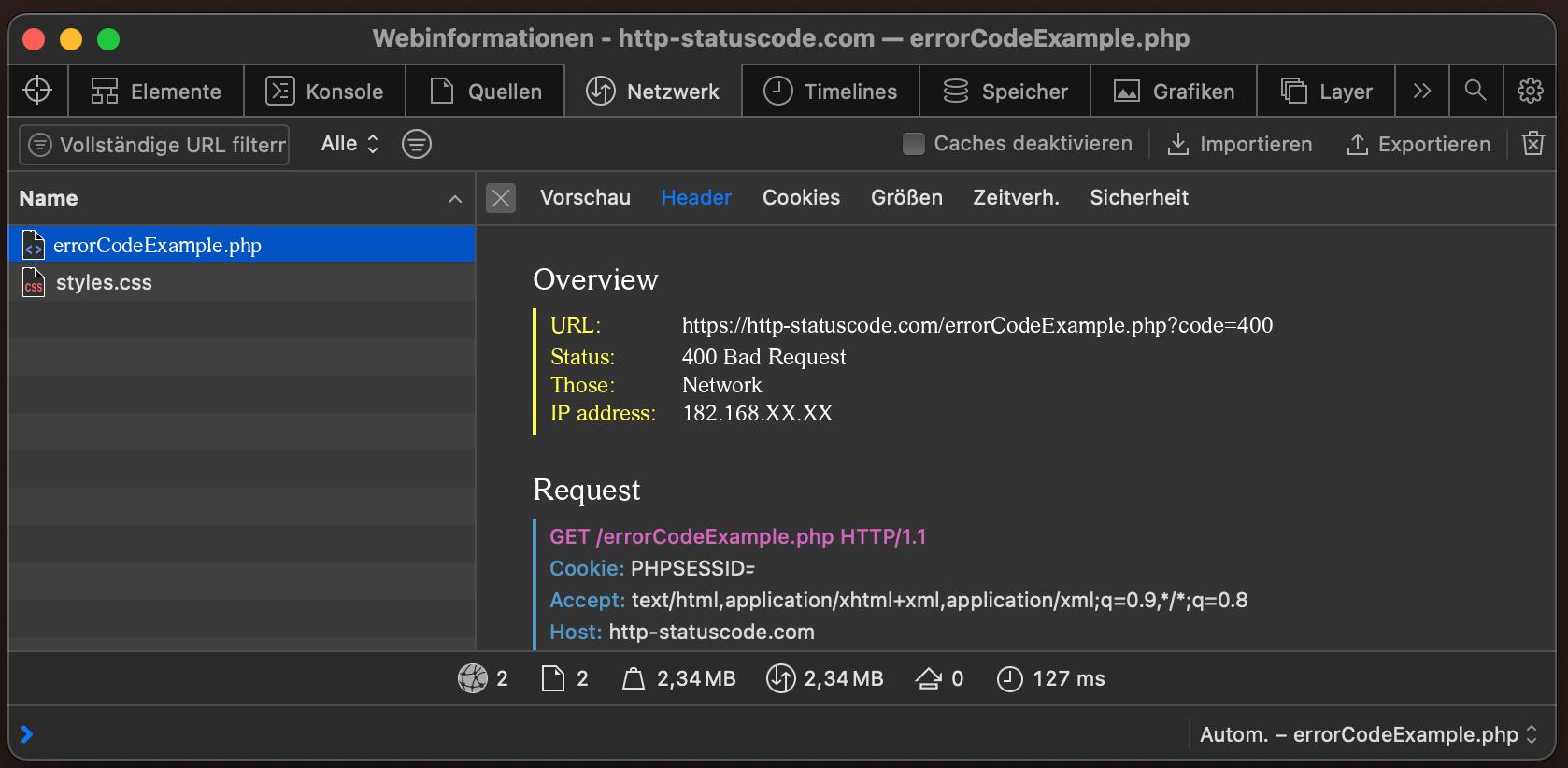
In order to be able to display the HTTP status code (in this case 400 Bad Request) and other information on the client side, the development console must be opened with F12. Afterwards you have to navigate to the tab "Network". Now you can open the page, in the network tab you should see the web page (example index.php). This must be selected and then the Herder section must be selected. Here the user will see the following result:
URL: https://http-statuscode.com/errorCodeExample.php?code=400
Status: 400 Bad Request
Those: Network
IP address: XX.XX.XX.XX
How to create a custom error page for the 400 status code
Apache Webserver
The web server "Apache" is one of the most popular web servers on the Internet. To create an own 400 Bad Request error page in "Apache", the following change must be made in the following file.
NGINX Webserver
Similar to the web server "Apache", "NGINX" is also widely used on the Internet. To create your own 400 Bad Request error page in "NGINX", the following change must be made in the following file.
location = /400.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
internal;
}
Browser compatibility of the 400 status code
| Chrome | no data |
| Edge | no data |
| Firefox | no data |
| Opera | no data |
| Safari | no data |
| Chrome Android | no data |
| Firefox for Android | no data |
| Opera Android | no data |
| Safari on iOS | no data |
| Internet | no data |
| WebView Android | no data |
Constants in programming languages
HttpStatusCode.BadRequest
:not_modified
http.StatusBadRequest
response::HTTP_BAD_REQUEST
httplib.BAD_REQUEST
http.client.BAD_REQUEST
http.HTTPStatus.BAD_REQUEST
:bad_request
Sub status codes of the 400 status code
| 400.1 | Invalid Destination Header HTTP IIS, Unofficial |
| 400.2 | Invalid Depth Header HTTP IIS, Unofficial |
| 400.3 | Invalid If Header HTTP ISS, Unofficial |
| 400.4 | Invalid Overwrite Header HTTP ISS, Unofficial |
| 400.5 | Invalid Translate Header HTTP ISS, Unofficial |
| 400.6 | Invalid Request Body HTTP ISS, Unofficial |
| 400.7 | Invalid Content Length 400, Unofficial |
| 400.8 | Invalid Timeout HTTP ISS, Unofficial |
| 400.9 | Invalid Lock Token HTTP IIS, Unofficial |
| 400.10 | Invalid X-Forwarded-For (XFF) header HTTP ISS, Unofficial |
| 400.11 | Invalid WebSocket request HTTP IIS, Unofficial |
| 400.601 | Bad client request (ARR) HTTP ISS, Unofficial |
| 400.602 | Invalid time format (ARR) HTTP IIS, Unofficial |
| 400.603 | Parse range error (ARR) HTTP IIS, Unofficial |
| 400.604 | Client gone (ARR) HTTP IIS, Unofficial |
| 400.605 | Maximum number of forwards (ARR) HTTP IIS, Unofficial |
| 400.606 | Asynchronous competition error (ARR) HTTP IIS, Unofficial |
